1.1.2 Cell Biology and Histology of the Vascular System Flashcards
Name the major vessels in the order in which they occur starting from the left ventricle.
Large (elastic) artery, medium (muscular) artery, small (ateriole) artery, capillary, venule, medium/large veins
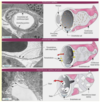
What are the three types of capillaries?
Continuous: (pericytes [modified smooth muscle cells] can occur b/t endothelium and basement membrance)
Fenestrated: pores or fenestrae in endothelium
Discontinuous: gaps b/t endothelial cells
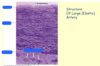
What are the 3 major layers of the walls of arteries?
- Tunica intima (innermost)
- Tunica media (middle)
- Tunica externa or adventitia (outermost)
How many tunics do veins have?
three tunics
Distinction b/t t. media and t. adventitia often unclear and a distinct internal elastic lamina is usually absent. T. media is thinner than that found in arteries of same diameter.
What protein aids in the transcytosis across a continuous capillary?
Caveloin; caveolae and vesicles transport substances through the cytoplasm in a bidirectional pathway

When you spend too much time making/studying flashcards and lose all of your gains….





Describe the tunica media.
Concentric layers of smooth muscle, collagen fibers, discontinuous plates of elastic sheaths (external elastic lamina)
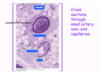


What is required for both vasculogenesis and angiogenesis?
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), VEGF receptors, and angiopoietins (Ang 1 and 2) and its receptor (Tie2)
What are some risk factors for atherosclerosis?
LDL levels, diabetes, HTN, age


Loss of pericytes will have what effect on the BBB?
Increases permeability of BBB in CNS. Pericytes are involved w/ tight junction formation
Oxidative stress leads to dysfunction of what type of cells and reduced bioavailability of what molecule?
Endothelial cells and reduced NO bioavailability
What is another term from large (elastic) arteries?
Conducting arteries, b/c they conduct blood from heart to the medium-sized ateries
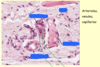
What type of capillary is each of these? What are the arrows pointing at?