Hemorhagicc stroke Flashcards
What are the risk factors for Intraparenchymal hemorrhage?
Hypertension Coagulopathy Vascular malformation (Aneurysm, AVM) Tumor (EG. Melanoma, Cerebral amyloid angiopathy)
Where is the usual locations of a hypertensive hemorrhage?
- Deep Gray Nuclei (Basal Ganglia, Thalamus)
- Pons
- Cerebellum
Pic: example of basal ganglia and talmus hemorhage

Example of pons and cerebellum image

What is a hemorhage at the grey white junction of the cerebrum suggestive of?
a underlying metastatic lesion

Cerebral amyloid angiopathy
ussually found in older patients

How do you manage a intraparachymal hemorhage?
- Blood pressure control
- Address coagulopathy
- Identify/address underlying structural abnormality
- Consider Neurosurgical decompression
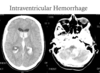
Interventricular hemorhage
hydrocephaly could be a problem
Subdural hematomal
low pressure-venous blood
blood is irritating to the brain
old people are ussally the problem because thier brain shrinks, recurents can happen

What is diagnostic of Epidural Hematoma?
- High pressure arterial bloodflow
- Middle Meningeal Artery
- Lucid Interval
lens shaped

What are risk factors of venous sinuses thrombosis?
Hypercoagulable
- Genetic
- Pregnancy
- Malignancy
- Inflammatory disease
- Infection
Pic: left side is venous rupture. bloody because blood cant leav via veins
Right: pale with cherry macula

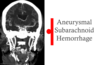
What is a thunderlap headche?
aneurysmal subarachnoid
Traumatic sub rachnoid

Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorhage?
Traumatic subarachnoid hemorhage

How are subarachnoid hemorhage diagnosed?
- Noncontrast CT
- If CT nondiagnostic–Lumbar puncture (Elevated RBCs in CSF, Elevated RBCs in tubes 1-4-if blood is in all tubes, Xanthochromia-pigment released from RBCs in the CSF, Consider repeating 6 hours after onset of symptoms)
- Angiography
What are complications of Subarachnoid hemorhage?
- Death- a lot die)
- Re-bleed (Early clip or coil)
- Seizure
- Hydrocephalus
- Vasospasm(Peak day 8)- irritation by blood, can have ishema stroke
- Nimodipine
- Pulmonary edema
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- Hyponatremia
