Harmless Lumps & Bumps Flashcards
What is this and what is the treatment?

Plane Warts
Treat with Topical retinoids, cryotherapy or imiquimod.
Cryotherapy can cause Koebnerisation.
What is this?
What is the treatment
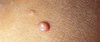
Molloscum Contagiosum
Treat with Molludab, topical imiquimod.
If a giant molloscum or many molloscums appear in an adult, what should you suspect?
Immunocompromise. (HIV etc)
What is this?
How is it treated?

Sebaceous Hyperplasia
- Removal with curretage, cauteryor excision
- Deep Peels with TCA also help.
How do you remove milia?
A green needle (to extrude the calcified contents)
What is this?
How is it treated?

Syringoma (Benign tumours of sweat glands)
Occur under the eyes
Often run in families
Best left alone
What is this?
How is it treated?

Pyogenic Granuloma
- Curettage and cautery BUT always send for histology.
Why must you always send pyogenic granulomas for histology?
Differential diagnosis of amelanotic melanoma
Where do pyogenic granulomas usually occur?
- Head
- Neck
- Upper trunks
- Hands
- Feet
What is the cause of pyogenic granulomas?
- Infection (usually Staph)
- Hormonal influences - pregnancy, COCP
- Drug induced (retinoids & Protease Inhibitors)
How are skin tags removed?
Snip Excision or Ablation
What is this?

Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra
(Think Morgan Freeman)
How are Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra treated?
Usually left alone.
If removed, consider low pwer hyfrecation after a test area.
What are these?
How are they treated?

Cherry Angiomas
(Campbell De Morgan Spots)
Harmless - best leftalone.
Where and at what age do Cherry Angiomas appear?
- 30 years old
- Tunk and proximal limbs















