Posterior Leg and Plantar Foot Flashcards
The popliteal artery branches into what 2 arteries in the leg?
-Posterior tibial -Anterior tibial (popliteal a. will pierce interosseous m. and give rise to anterior tibial)
What artery supplies the anterior leg?
Anterior tibial a. (branch off popliteal a.)
What arteries supply posterior and lateral leg?
- Posterior tibial a. - Fibular a. (branch off of posterior tibial a.)
What veins supply the anterior leg?
anterior tibial vein
When veins supply the posterior and lateral leg?
- Posterior tibial vv. - Fibular v.
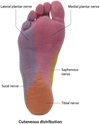
What nerve supplies cutaneous innervation the the anterior and medial leg?
Saphenous n. (from femoral n.)
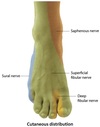
What nerves supply cutaneous innervation to the posterior and lateral leg
- Common Fibular n. - Sural n. (from tibial and common fibular n.)
Origin and insertion of Gastrocnemius
O: (M) posterior femur superior to medial condyle (L) Lateral femoral condyle
I: Posterior calcaneus

Innervation and action of gastrocnemius
N: Tibial
A: Plantarflexes foot, flexes leg

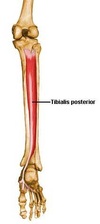
Origin and insertion of soleus
O: Soleal line of tibia; posterior fibular head
I: Posterior calcaneus

Innervation and action of soleus
I: Tibial n.
A. Plantarflexes foot

What nerve passes deep the tendinous arch of the soleus?
Tibial n.; Posterior a./v.
Origin and insertion of plantaris
O: Lateral supracondylar line of femur
I: Posterior calcaneus
*absent if 5-10% of people

Innervation and action of plantaris
N: Tibial n.
A: weakly plantarflexes ankle
When tendon in the posterior leg can be harvested and used for tendon grafts in the hand
Plantaris
Origin and Insertion of Popliteus
O: Lateral Condyle of femur and lateral meniscus
I: Posterior tibia

Innervation and action of popliteus
I: Tibial n.
A: Flexes knee; “unlocks” knee
Origin and insertion of flexor hallucis longus
O: Posterior fibula and interosseous membrane
I: Plantar surface of distal phalanx of hallux

Innervation and Action of flexor hallucis longus
I: Tibial n.
A: flexes hallux
Origin and insertion of Flexor Digitorum Longus
O: Posterior tibia
I: Plantar surface of distal phalanges of digits 2-5

Innervation and Action of Flexor Digitorum Longus
N: Tibial n.
A: Flexes digits 2-5