Neuroanatomy 3 Flashcards
(65 cards)
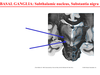
what are the three layers of the meninges
dura mater, arachnoid, pia mater
what are the two layers of the dura mater and what do they do
periosteum - anchors dura mater to skull meningeal dura - mechanical support and strength to brain
which layer of the dura mater is in the vertebral column
meningeal dura
where are the venous sinuses found
between the layers of dura mater and separate left and right hemispheres, as well as occipital lobe from the cerebellum
what are the venous sinuses filled with
venous blood
where are the potential spaces and what kind of blood vessel can fill it
epidural space (superficial to peristeom) - meningeal artery subdural space (deep to meningeal layer) - bridging veins
where are the real spaces
-between periosteal and meningeal layer - sagittal fissure - transverse fissure (separates occipital and cerebellum) - venous sinuses
describe the pathway of cerebral spinal fluid
made in lateral ventricle interventricular foramina of Monro 3rd ventricle cerebral aquaduct 4th ventricle foramina magendie –> cisterna magna foramina luschka –> pontine cistern subarachnoid space arachnoid granulations dural venous sinuses

where are the other areas that CSF goes in the body besides the cortex
superior cistern, interpeduncular, pontomedullary, cisterna magna, and lumbar (see lecture for picture)
what is non-communicating hydrocephalus
when flow of CSF is obstructed in the ventricular system
what is a communicating hydrocephalus
when the absorption of CSF is not sufficient to remove fluid being produced
what are arachnoid granulations. what kind if pressure is needed
protrusion of arachnoid into the venous sinus where the CSF in the subarachnoid space can drain into the venous sinuses. CSF pressure must be greater than venous pressure
what are the three most common brain herniations
subfalcine, uncal, tonsilar
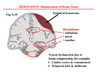
what is this

epidural hematoma
what is this
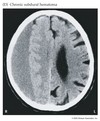
subdural hematoma
what is this
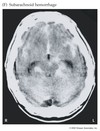
subarachnoid hemorrhage
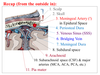
describe the full layers from the scalp to the pia mater
a subfalcine herniation compresses which part of the brain
limbic cortex and comissural
an uncal herniation compresses which brain structures
temporal lobe and midbrain
what are the three layers of the blood brain barrier
arachnoid barrier, choroid/blood CSF barrier, and actual BBB
how does the arachnoid barrier work
arachnoid granulations are considered one-way valves to prevent venous blood from subarachnoid space
how does the blood-CSF barrier
choroidal blood capillaries have fenestrations but tight junctions at the choroid epithelium that prevents blood from entering ventricles
how does the blood brain barrier proper work
tight junctions at the capillary level with astrocytes to help
where is an area where there is no BBB
pineal gland